Incorporating fundamental AI design principles is essential for creating user-centered experiences. These guidelines enhance interaction, build trust, and ensure ethical practices.
Table of Contents
AI has become a popular buzzword, often clouded by misconceptions and questions about its purpose and potential.
While ethical and philosophical challenges are well-known, AI can also create exceptional user experiences.
This article explores what AI is, its current state, and the unique design challenges experts face when building AI-driven experiences.
As AI continues to shape the future of user experience, now is the perfect time to dive into this field and understand its complexities and possibilities.
Tired of losing customers due to an outdated, clunky design?
Let’s work together to elevate your product’s design. I take on only a few clients at a time, so reach out today before spots fill up!
What is AI 🤖 (Artificial Intelligence)?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a branch of computer science focused on creating machines and software that can perform tasks typically requiring human intelligence.
These tasks include learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and natural language understanding.
AI systems range from narrow AI, designed for specific functions such as speech recognition or image analysis, to more theoretical general AI, which would have a broader, human-like understanding and adaptability.
How Does AI Compare to Human Intelligence?
AI and human intelligence have distinct strengths and limitations, making them complementary in many ways:
- Speed and Efficiency: AI can process vast amounts of data at speeds far beyond human capabilities, making it highly useful for tasks such as data analysis, pattern recognition, and automation. For example, AI can analyze thousands of medical images in seconds, helping doctors diagnose faster.
- Learning and Adaptability: Human intelligence is more flexible. People can learn from a few examples, transfer knowledge across domains, and navigate complex social interactions. AI, however, often requires extensive training data and is generally less adaptable to new, unforeseen circumstances. Human intuition and common sense, which develop through lived experience, are also challenging for AI to replicate.
- Creativity and Emotions: Humans excel in creativity, imagination, and emotional understanding. While AI can mimic specific creative processes, like generating artwork or music based on patterns, it lacks genuine emotional experience and self-awareness. Human intelligence is driven by curiosity, emotions, and personal motivations that give depth to creativity and problem-solving.
- Problem-Solving and Contextual Understanding: AI is highly specialized and effective within narrow domains but struggles with contextual understanding and the nuanced, multi-layered decision-making that humans handle effortlessly. While AI might be skilled at playing specific games or analyzing text, it doesn’t understand the broader implications or context of its actions the way humans do.
- Ethics and Morality: Human intelligence includes an understanding of ethics, empathy, and moral reasoning, which guide behavior beyond purely logical decision-making. Conversely, AI operates based on programmed instructions and data, lacking intrinsic ethical judgment.
Can AI Compete with Human Intelligence?
AI can outperform humans in some specialized regions—especially when speed, data analysis, and pattern recognition are paramount. However, AI lacks the holistic, adaptive, and deeply contextualized understanding that characterizes human intelligence.
While AI may augment and extend human abilities, it cannot compete with or fully replicate human thought’s complex, multi-dimensional nature.
The Future: Complementary Roles
Rather than directly competing with human intelligence, AI will likely be a powerful tool that complements and enhances human capabilities.
AI can support humans in medicine, education, finance, and the creative industries by taking over repetitive tasks, providing insights from large datasets, and enabling innovation.
AI and human intelligence have distinct strengths, and their combined power may yield transformative possibilities. This is why we should embrace AI as a Product UI/UX Designer.
AI Design Principles
Technology is on an unstoppable march forward, disrupting our lives in ways we can’t even imagine (like how many cat videos we can watch before our brains short-circuit).
As part of the creative community, we’re in the driver’s seat, steering what AI might become. We’re laying the foundation for something that could be spectacular—or, you know, setting ourselves up for a sci-fi horror movie.
But here’s the good news: we’re at the dawn of an AI-driven era! Instead of getting lost in extremes about what the future might hold—like whether AI will be our trusty sidekick or our overlord—let’s focus on how we can team up with AI and what guiding principles can help this technology scale up without sending us all into a tailspin.
The million-dollar question (or, in the case of AI, maybe a billion-dollar question) is: what should those design principles be? Since AI is constantly evolving, it’s a bit like trying to hit a moving target while blindfolded.
However, we’ve gathered some insights from the experts, focusing on concepts and user interfaces, to give us a fighting chance in this brave new world. Let’s dive in!
1. Minimal Effort, Maximum Impact
In today’s world, decision fatigue is a daily struggle. Notifications, endless choices, and constant demands pull our attention in every direction. This is where AI steps in as the quiet assistant, taking on the background work that frees us up to focus on what truly matters. Imagine those small, repetitive tasks that AI can handle seamlessly, leaving us with fewer decisions and more mental space.
The challenge is to think beyond functionality—design experiences where users feel the impact with barely any effort on their part. Aim to solve meaningful problems while demanding minimal engagement, creating a smoother, more innovative experience.
EXAMPLES
– Spotify’s Personalized Playlists

- How It Works: Spotify’s AI generates playlists like “Discover Weekly” and “Release Radar” based on individual listening habits, favorite genres, and trending music. The AI suggests songs that match personal preferences without requiring users to search for new music manually.
- Impact: With little to no effort, users enjoy fresh, curated music tailored to their tastes, discovering new artists and songs without endless browsing.
– Amazon’s “Buy Again” and Reorder Suggestions
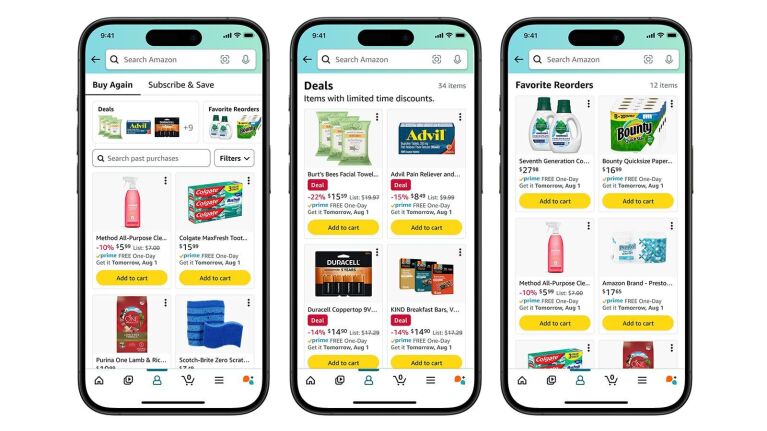
Image Credits – Amazon
- How It Works: Amazon leverages AI to track past purchases and suggest items customers frequently reorder. The “Buy Again” feature allows users to repurchase essentials quickly with just a few clicks.
- Impact: By predicting what users want to reorder, Amazon minimizes searching time, making everyday shopping faster and more intuitive.
2. Design for Accepting Mistakes
Let’s face it: AI is going to mess up sometimes—a lot of times.
If we trust AI, we must accept that it will be less than perfect.
So, how do we cope with these little blunders? Well, there are a few tasty ingredients to consider. First up, sprinkle in a dash of humor!
Imagine if your digital assistant apologizes for misreading your command by saying, “Oops! You said, ‘Play elevator music,’ not ‘Help me find a pizza.’ My bad! Let’s try again!” A chuckle can turn frustration into forgiveness.
Another vital ingredient is giving users a voice. Functionality that allows users to provide feedback is essential.
EXAMPLES
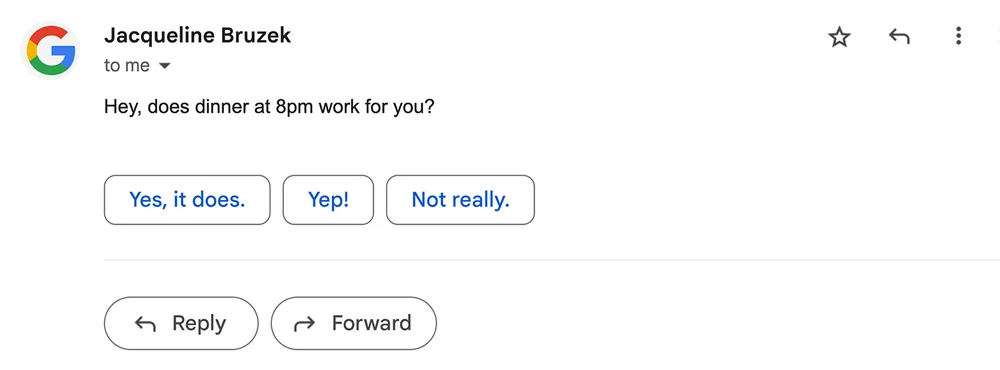
- Email services like Gmail provide intelligent suggestions for replying. If the AI misinterprets the context and suggests a reply that doesn’t fit, it might include a lighthearted comment like, “Not quite what you meant? Just say the word, and I’ll find something better!”Impact: By acknowledging the potential for misinterpretation and offering to correct it, users feel supported and are more likely to interact with the feature again.
- Google Assistant often acknowledges when it mishears or misinterprets commands. If you ask it to play “Lady Gaga” and it starts playing “Elevator Music,” it might respond with, “I’m sorry! I must have hit the wrong note there. Let’s try again!” This humorous acknowledgment softens the blow of a mistake and reminds users that the assistant is learning and improving, encouraging them to give it another shot.
These strategies help create a more forgiving environment where users feel empowered and engaged, even when the AI stumbles. After all, if we can laugh off a bad joke or offer constructive feedback after a hiccup, we’re much more likely to stick around for the good stuff. So, let’s embrace the messiness of AI and design with a spirit of forgiveness!
3. Design for Trust: AI in Practice
First off, transparency is key! Users should know exactly what data you’re collecting and how it’s being used. Imagine logging into a new app and seeing a friendly pop-up that says, “Hey there! We’ll be using your data to recommend the best cat videos.
Don’t worry; we won’t tell your boss you’re spending your lunch break on YouTube!” A little humor goes a long way in easing those data-sharing anxieties.
Another important aspect is giving users control over their data. They should be able to modify or delete their information whenever they want.
Picture a scenario where users can adjust their preferences, saying, “Sure, I love cats, but let’s take a break from the cat videos and switch to some cute puppies for a while!”
This kind of control not only empowers users but also builds trust. They’ll feel like they’re not just data points but valued participants in the AI conversation.
EXAMPLES
Creating a healthy dynamic where transparency and honesty are the cornerstones is vital. A great example is Apple, which proudly emphasizes its commitment to user privacy.
Their privacy policy reads like a love letter: clear, concise, and free from legal jargon that sounds like it was written by a robot with a PhD in gobbledygook. Users appreciate knowing their data isn’t tossed around like a hot potato.
Then there’s Netflix, which is transparent about how it uses viewing history to recommend content. It might say, “We track what you watch to keep your binge-watching habit well-fed with the latest sci-fi thrillers and rom-coms.”
This openness helps users feel comfortable, knowing their data is used to enhance their viewing experience rather than sold to the highest bidder.
Finally, let’s not forget the importance of building trust through honest communication. If an AI system encounters a hiccup or makes a mistake, it’s crucial to acknowledge it.
For instance, if your virtual assistant misunderstands your command and starts playing polka music instead of your favorite playlist, a friendly, “Whoops! Looks like I need to recalibrate my ears! Let’s get back to those smooth jazz vibes!” can make all the difference.
4. More Human-Friendly Experiences
As our daily interactions with machines evolve at breakneck speed, the importance of infusing personality into these experiences has never been more evident.
EXAMPLES
A fascinating study by Google examined how users interacted with Google Home, and one thing stood out: people were treating it like a fellow human! Users often said “thanks” or even “sorry” after issuing a voice command.
This charming behavior highlights a powerful insight: when devices possess a hint of personality, it deepens the human-machine relationship.
People naturally connect more with devices that feel personable, as if they’re not just talking to a piece of technology but engaging with a friendly companion.
Imagine if your intelligent assistant greeted you each morning with a cheerful, “Good morning! Ready to conquer the day?” or offered a comforting, “Oops, my bad!” when it misunderstood your request.
Such interactions make technology feel more approachable and less like an impersonal tool, encouraging users to engage more openly and frequently.
By humanizing our experiences with technology, we pave the way for more meaningful connections—turning mundane tasks into delightful interactions!
5. Design for Fewer Options
In the fast-paced world of AI-driven experiences, we often find ourselves drowning in a sea of choices.
Every app tries to be the Swiss Army knife of the digital world, throwing options at us like confetti at a parade!
But here’s the kicker: too many choices can overwhelm users, like a kid in a candy store who’s suddenly allergic to sugar.
Currently, most products are reactive—like a cat that only jumps into your lap when it wants something. You must issue a command, wave your hands like a magician, or press a button to get them to do their job.
But imagine a future where AI proactively triggers actions—like your virtual assistant popping up to say, “Hey, it looks like you’re about to forget your meeting. Shall I set a reminder or bring you coffee?”
So, how do we design for fewer choices? The answer is simple: eliminate unnecessary decisions.
Think of it this way: if your app suggests a million things for dinner, it might be time to step back and ask yourself, “Is this really helpful, or am I just making users want to throw their phones out the window?”
EXAMPLES
Take Spotify, for instance. Instead of bombarding you with every possible playlist, it curates a “Daily Mix” that reflects your listening habits—like a DJ who knows your favorite jams but doesn’t make you sift through a million tracks to find them.
This thoughtful design creates headspace for users, allowing them to focus on what truly matters—like singing along to “Bohemian Rhapsody” in the shower.
Then there’s Amazon, which has mastered the art of less choice with its “Buy Now” button.
You don’t want to scroll through fifty options when you find that perfect pair of socks. Instead, Amazon makes it as easy as one click—like magic!
Who has time to decide between “fuzzy” and “extra fuzzy” when you all want comfort?

Finally, think of how Google Maps simplifies navigation. Instead of asking if you want to avoid tolls, traffic, or scenic routes every single time, it just gets you there the fastest way possible. “You’ll thank me later when you’re not stuck behind that school bus!”
Here are some additional AI design principles that can be particularly beneficial for SaaS Product UI/UX designers:
7. Emphasize Transparency
- Principle: Be open about how AI works and what data it uses. Users should understand how their information is processed and the rationale behind AI decisions.
- Example: In a finance app, when AI suggests budget changes, provide a simple explanation of how it arrived at those suggestions, such as “Based on your spending in the last month, we think you can save more by cutting back on dining out.”
8. Provide Explainability
- Principle: Explain AI-generated outcomes. Users should not just see results; they should understand how they were derived.
- Example: If an AI-based resume reviewer recommends changes, include a feature that highlights which keywords or phrases are missing compared to those of successful applicants.
9. Encourage User Feedback
- Principle: Design interfaces that allow users to give feedback on AI suggestions or actions. This not only helps improve the AI but also builds user trust.
- Example: After a navigation app reroutes users, prompt them with a simple “Did this route work for you?” to gather feedback on the AI’s performance.
10. Design for Inclusivity
- Principle: Ensure AI systems accommodate diverse user needs, preferences, and abilities. Avoid assumptions based on average behaviors or profiles.
- Example: When creating an AI chatbot, include options for voice commands, text input, and visual cues for users with different accessibility requirements.
11. Prioritize User Control
- Principle: Empower users by giving them control over AI features and settings. Users should be able to adjust how AI interacts with them based on their preferences.
- Example: In a smart home app, allow users to customize how their device responds to voice commands, like “I want it to only respond to my voice” or “Let’s keep the light dim during movie nights.”
12. Utilize Anticipatory Design
- Principle: Anticipate user needs based on their behavior and context. AI should offer solutions before users even realize they need them.
- Example: A travel app that analyzes a user’s booking patterns and suggests trips or accommodations based on previous preferences without the user having to search.
13. Balance Automation with Human Touch
- Principle: While AI can automate tasks, it ensures an option for human interaction when needed. Some users may prefer personal assistance over automated responses.
- Example: In customer service, allow users to quickly escalate from an AI chatbot to a human agent if their query is too complex.
14. Ensure Ethical Considerations
- Principle: Integrate ethical considerations into the design process to avoid biases in AI algorithms and ensure fairness in AI decisions.
- Example: Conduct regular audits on algorithms used in hiring platforms to ensure they don’t favor specific demographics over others based on historical data biases.
15. Iterate and Adapt
- Principle: Treat AI systems as evolving entities that can learn from user interactions and feedback. Regularly update and refine the design based on actual user data.
- Example: In an AI-based news aggregator, continually adjust the types of articles shown based on what users read, share, or skip over time.
By incorporating these principles into your SaaS design practice, you can create more user-friendly, ethical, and effective AI-powered interfaces that enhance the overall user experience.
Balancing user needs with AI’s capabilities will lead to more engaging and trustworthy interactions.
AI is everywhere.
Examples and Use Cases!
Yes, AI is woven into many aspects of our daily lives, often in ways we might not even notice. Here are some key examples of how AI plays a role in everyday activities:
1. Smartphone Assistance 📱
- Voice Assistants (e.g., Siri, Google Assistant, Alexa): AI-driven voice assistants respond to spoken commands, answer questions, set reminders, and control smart home devices. They use natural language processing (NLP) to understand and respond to requests, making it easier to interact with technology hands-free.
- Photo Management: Many smartphones use AI to categorize photos, recognize faces, and suggest ways to improve image quality. For example, Google Photos and Apple Photos use AI to automatically organize images by people, places, and events.
- Autocorrect and Predictive Text: AI algorithms learn from user typing patterns to suggest words, correct spelling errors, and predict what you want to type next. This feature streamlines communication and makes typing faster and more efficient.
2. Social Media Platforms 📢
- Content Recommendations: Social media platforms like Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, and TikTok use AI to analyze user preferences and behaviors and recommend content, from posts and videos to ads. AI optimizes what you see on your feed based on past interactions to keep you engaged.
- Image Recognition and Tagging: AI automatically identifies people and objects in photos, allowing users to tag friends and categorize content. Platforms like Facebook use image recognition to suggest tags and help organize content.
- Language Translation: AI-powered translation features on social media, such as those on Facebook and Instagram, allow users to instantly translate posts and comments into different languages, fostering communication across language barriers.
3. E-Commerce and Online Shopping 🛍️
- Personalized Recommendations: E-commerce platforms like Amazon use AI algorithms to analyze browsing and purchase history, recommending products tailored to your interests. These algorithms also consider trends, customer ratings, and other data points to improve accuracy.
- Chatbots and Customer Service: Many online retailers use AI-driven chatbots to assist customers with product inquiries, order tracking, and troubleshooting. These chatbots are often available 24/7 and can handle multiple queries simultaneously, improving response times and customer satisfaction.
- Dynamic Pricing: AI adjusts prices in real-time based on demand, competition, and other factors. For example, airlines and hotel booking sites use dynamic pricing to offer competitive rates based on customer demand and booking timing.
4. Finance and Banking 🏦
- Fraud Detection: Banks and financial institutions use AI to monitor transactions for unusual patterns that may indicate fraud. For example, if an atypical transaction is detected, the bank may block it or send an alert to confirm its legitimacy.
- Customer Support: AI chatbots and virtual assistants help customers check their account balances, pay bills, or answer questions about their accounts. For example, Bank of America’s virtual assistant, Erica, assists users with various banking tasks.
- Loan and Credit Approval: AI is also used to assess creditworthiness and evaluate loan applications. By analyzing financial histories and risk factors, AI can make more accurate assessments and speed up the approval process.
5. Navigation and Transportation📍
- GPS and Traffic Prediction: Applications like Google Maps and Waze use AI to analyze traffic patterns and suggest the quickest route. AI considers current traffic, accidents, and weather conditions to provide accurate ETAs and suggest alternate routes.
- Ridesharing Apps (e.g., Uber, Lyft): AI powers ride-hailing services by matching drivers and riders, predicting demand surges, and calculating estimated arrival times. These platforms use AI to optimize routes and suggest pick-up and drop-off points based on traffic and location data.
- Self-Driving Cars: Although still in development, self-driving cars like Tesla use AI to recognize road signs, pedestrians, and obstacles, navigate traffic, and make real-time decisions to operate safely without human intervention.
6. Home Automation 🏠
- Smart Home Devices: AI powers smart home devices like thermostats (Nest), lighting (Philips Hue), and security systems (Ring). These devices learn from user behavior to create personalized settings, such as adjusting the temperature based on preferences or turning lights on/off based on activity.
- Voice-Controlled Assistants: AI-driven devices like Amazon Echo and Google Home can control multiple smart home devices, from lights to security systems, all through voice commands.
- Energy Management: Some AI-powered systems analyze energy usage to optimize consumption, potentially lowering utility bills. For example, smart thermostats use AI to learn when to adjust the temperature based on daily routines.
7. Email and Communication 📨
- Spam Filters: Email platforms like Gmail use AI to filter out spam and phishing attempts. AI algorithms analyze email content, sender reputation, and user behavior to identify and filter unwanted messages.
- Smart Replies and Email Categorization: Gmail’s “Smart Reply” feature suggests quick email responses, while the categorization feature organizes emails into categories like Primary, Social, and Promotions based on content. These AI features make managing email faster and more intuitive.
- Grammar and Writing Assistance: Tools like Grammarly use AI to offer grammar suggestions, style improvements, and tone adjustments, helping users communicate more effectively.
8. Health and Fitness 🏃
- Health Monitoring Apps: Fitness apps like Apple Health and Google Fit use AI to track physical activity, sleep patterns, and even heart rates, offering insights into users’ health and fitness.
- Wearable Devices: Smartwatches (e.g., Apple Watch, Fitbit) monitor health metrics like heart rate, oxygen levels, and steps taken. These devices use AI to interpret data, detect anomalies, and sometimes alert users of potential health issues.
- Telemedicine and Symptom Checkers: AI-powered telemedicine platforms offer virtual health consultations and use symptom-checking algorithms to help patients determine if they need further medical care.
These examples highlight just how embedded AI is in our day-to-day lives. As AI advances, it’s becoming an indispensable part of our interactions, helping us communicate, stay organized, make decisions, and even monitor our health.
Crafting Intelligent Experiences: Where AI Meets Human-Centric Design
As creators, we seek new approaches to shape our products and services. Artificial Intelligence transforms how people interact with these creations and influences our design process.
The potential for AI is vast, with the power to deliver meaningful experiences. However, we’re currently in the era of narrow AI, where AI is adept only at performing specific tasks. This allows AI-driven products and services to enhance designers’ capabilities in targeted areas.
Experts in both design and AI are actively exploring best practices for designing with AI—focusing on key considerations, guiding principles, and ethical standards to follow.
How can AI help in a creative process?
AI can be a powerful tool in the creative process, acting as both a collaborator and a source of inspiration. Here are some key ways AI can enhance creativity across various fields:
1. Idea Generation and Inspiration
- Brainstorming New Ideas: AI can generate a range of concepts from existing data, helping creatives quickly explore new directions. For example, AI tools such as GPT-based models or image-generation models (DALL-E) can provide text or visual prompts that inspire unique concepts or design ideas.
- Mood Boards and Visual Styles: Designers can use AI to create mood boards or to visualize different styles and themes quickly. AI can analyze visual trends or generate variations based on specific prompts, helping artists explore diverse aesthetics they may not have considered.
2. Automated and Assisted Design
- Graphic and Layout Design: AI-powered tools like Adobe Sensei assist with image editing, layout optimization, and color selection, saving designers time on routine tasks and allowing them to focus on the larger creative vision.
- Generative Design: AI can generate multiple design variations based on constraints such as architectural and product design. This generative approach helps designers explore options they may not have considered, often leading to innovative forms and structures.
3. Personalization and Audience Insights
- Content Personalization: AI can analyze audience data to tailor content to specific user preferences. For example, content creators can use AI to adjust tone, style, or visuals based on user segments, enhancing engagement and relevance.
- Audience and Trend Analysis: AI-driven insights from social media, customer reviews, and other online data sources help creatives identify emerging trends and understand audience preferences. This data can inspire more targeted, resonant creative choices.
4. Enhanced Storytelling and Writing Assistance
- Story Development: AI tools can help writers develop plots, characters, and dialogue by generating ideas or filling in gaps in their stories. Writers can use tools like ChatGPT to brainstorm or explore alternative narratives and character arcs.
- Editing and Style Suggestions: AI writing assistants like Grammarly or Hemingway offer grammar, style, and tone suggestions, helping writers refine their work to match their intended voice or audience. This feedback can improve the clarity and impact of written content.
5. Music and Audio Creation
- Music Composition: AI-based platforms such as AIVA and OpenAI’s MuseNet can compose music in various styles based on input parameters. Musicians and composers can use these AI compositions as a foundation, remixing or layering them to create original pieces.
- Sound Design: AI tools help sound designers create soundscapes, effects, and ambient music to complement films, games, and other media. AI-based audio manipulation allows for quick experimentation with tones and rhythms.
6. Collaborative Creativity and Co-Creation
- Interactive Collaboration: AI tools enable artists and designers to collaborate with the software, receiving real-time feedback or suggestions. For example, artists working in AI-powered digital art programs can receive instant color or pattern recommendations.
- Cross-Disciplinary Fusion: AI makes collaborating easier for creatives from different disciplines by providing a common platform. For instance, an artist and a programmer might co-create an interactive installation where AI-driven interactivity coded by the programmer augments the artist’s visuals.
7. Rapid Prototyping and Experimentation
- Design Prototypes and Mockups: AI can quickly generate mockups based on wireframes or sketches, giving designers a tangible preview of their ideas. This helps in the rapid iteration and testing of design concepts, speeding up the creative process.
- Testing Creative Variations: For marketers and advertisers, AI enables quick A/B testing by generating different versions of content, such as social media ads or website layouts. This allows teams to identify what resonates best with their audience.
8. Overcoming Creative Blocks
- Idea Expansion: AI can help creatives overcome blocks by suggesting ideas based on the themes they’re working with and providing alternative perspectives or storylines that might not otherwise come to mind.
- Revisiting and Remixing Existing Work: AI can analyze previous works to suggest new variations, compositions, or edits. For example, an artist can input an existing painting or design, and the AI might offer fresh takes, pushing them to explore new creative directions.
AI doesn’t replace the artist’s vision but is a supportive tool that augments creativity, accelerates processes, and inspires innovative solutions.
By leveraging AI in this way, creatives can blend human intuition and machine-driven insights, opening new realms of possibility.
