Like an inseparable couple (rider & cycle), UX and UI seem to merge into an undifferentiated unit in the perception of many. They are usually only mentioned collectively and thus seem difficult to distinguish from one another. The two disciplines are actually more in a mother-daughter relationship.
Let's find out together what is UI and UX.
UI (User Interface) and UX (User Experience) are two terms that are often used together in the context of digital product design.
UI refers to the visual and interactive aspects of a product, such as a layout, typography, colors, buttons, and icons. It's the look and feel of a product, and it's part of the product that users interact with directly.
UX, on the other hand, is all about how a user interacts with and experiences a product. It's the overall journey that a user goes through when interacting with a product, including their emotions and perceptions. UX design encompasses a wide range of design disciplines, including information architecture, interaction design, and usability testing, to create a seamless and intuitive experience for users.
In short, UI is about how a product looks and functions, while UX is about how a user interacts with and experiences a product. Both UI and UX are critical elements of digital product design, and they work together to create an overall enjoyable and effective user experience.
In the following, I would like to explain to you why the two need each other but are still independent complexes.
Importance of UI/UX design
User Interface (UI) and User Experience (UX) design are critical components of software design because they help to determine how easy or difficult it is for users to interact with and use a product.
Here are some of the key reasons why UI/UX design is important:
Improved User Satisfaction: Good UI/UX design can greatly enhance the overall user experience, leading to increased user satisfaction and loyalty.
Better User Adoption: When a product is designed with a strong focus on UI/UX, users are more likely to understand and adopt it, increasing its overall effectiveness.
Increased Productivity: A well-designed user interface can streamline processes and reduce the time it takes to complete tasks, increasing overall productivity.
Better Conversion Rates: A product with a positive user experience is more likely to convert casual users into paying customers.
Competitive Advantage: Companies that prioritize UI/UX design can gain a competitive advantage by offering a more enjoyable and effective product experience compared to their competitors.
Better Accessibility: UI/UX design can also improve accessibility for people with disabilities, making products usable for a wider range of users.
In short, UI/UX design plays a critical role in the success of a product by improving the user experience, increasing adoption and productivity, and providing a competitive advantage.
For a start-up or a small venture, the importance of UI and UX Design becomes even more crucial as the first impression lasts long, and using UI and UX designing can make or break brand recognition.
Key components of UI/UX design

There are core components of UI/UX design, which are as follows:
1. Information Architecture
Information Architecture, also known as the IA, is all about satisfying the business strategies by designing the application’s or the site’s information structure. The major role of the IA is to provide its users with easy navigation no matter which browser they are using. It’s about using the maximum permutations and combinations to provide the best and a top-level navigation menu.
2. Interaction Design
Interaction Design is about creating the conceptual design with which the users interact with the product and/or application. This interaction includes various elements such as aesthetics, color, font, icons, images, motion, sound, space, graphics, etc.
3. Usability
Usability can be referred to as user-friendliness as well. Along with figuring out if the users get the information they want by using the application or visiting the site for the first time and if the application/website is easy to navigate, the usability also comprehends the ways to handle the errors.
4. Wireframing
Wireframing is about creating a sample of the application to test the features, look, and usability of the application before it is actually launched. It is a cheap way to test functionality and evaluate if the application serves its purpose.
5. Visual Design
The visual design of the application or the website is like defining the company’s brand. Finalizing the visual design can affect the users’ behavior and hence it is the most important component of the UI design. Visual Design is not only about selecting the best images, colors, icons, and fonts, but also identifying the appearance of the application that impacts the interaction of its users.
Now that you are aware of the UI/UX components!!!
6. Reasons Why Your App needs an Efficient Ul/UX design
Well, Coming up with an efficient Ul/UX design for an app is always a priority for most app owners. This requires thorough research and prior planning in order to understand the needs of your users and the problem you intend to solve with your app. Regardless of your needs, you will have to come up with a design that works.
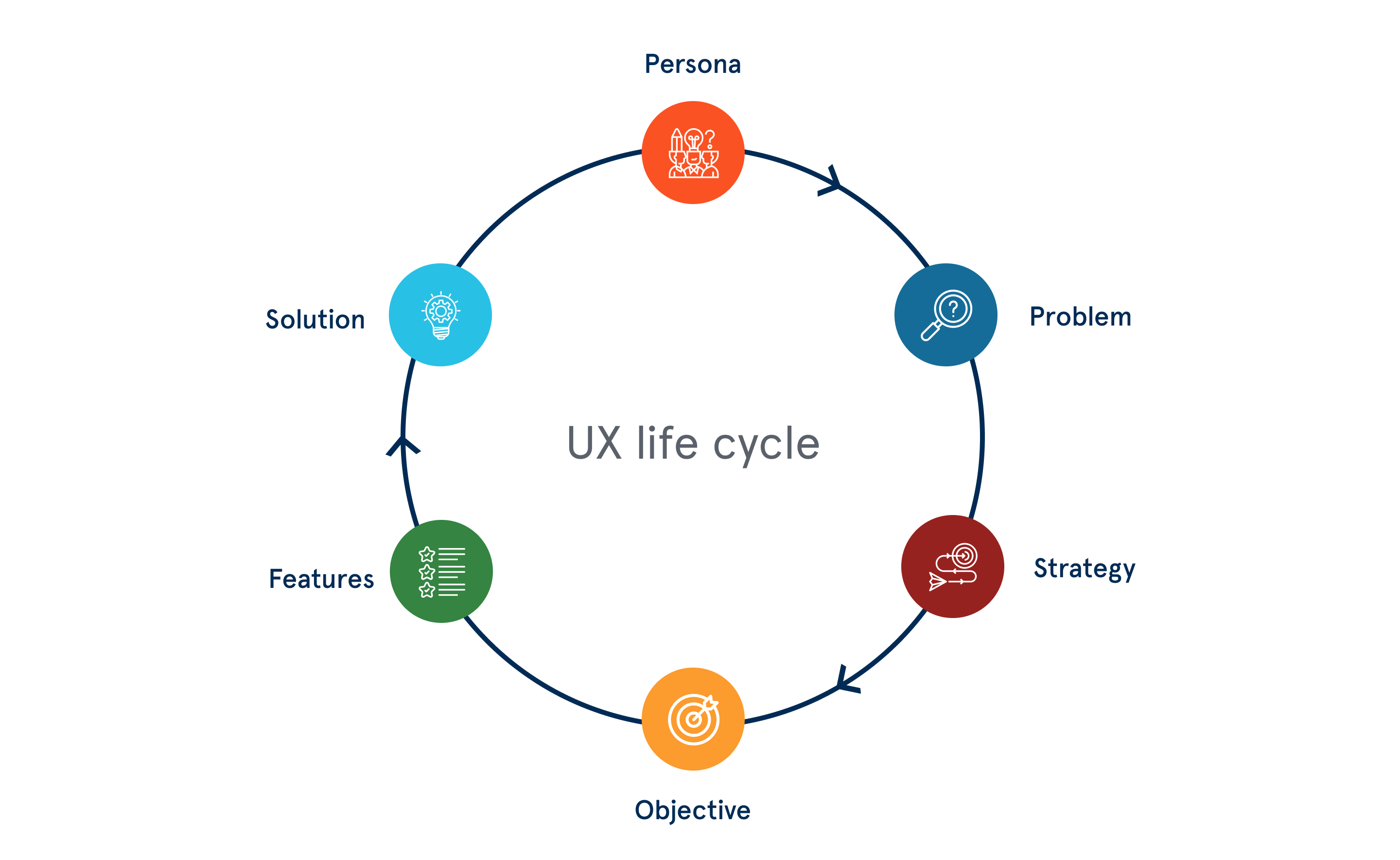
What is UX?
User experience design - in short: UX design
First of all, the meaning of the name as such: UX, i.e. the so-called user experience (or user experience design ) is the more comprehensive value of the two, i.e. the basis (mother).
Experience is everywhere
The user experience is actually not as new as the job title suggests. It has only acquired a completely new status through the extensive planning of online applications. The term “experience” covers everything that the user perceives during use.
It doesn't necessarily have to be in the digital space. Be it a visit to a museum or opening a milk carton: These two “interactions” also encompass a user experience.
All of this is about the same thing: Does the user understand the communication within my product/application and how is it doing?
So a canned food or an innovation?
That is why, from my point of view, both disciplines are always a mixture of what has been learned and innovation. How many innovative ideas can I put in a milk carton and how much on a website? How do I avoid museum visitors only finding their way to the toilets and not to my new permanent exhibition, and how do I ensure that users of my app simply get the information they need at all times?
Clear guiding principle: Think about your users
In contrast to some politicians, we do not believe that the Internet is new territory and yet we always want to make getting started with a web application as easy and meaningful as possible. That also means: I need empathy for my target group and a view from different user perspectives.
Some things have already been learned. So you probably know that when you visit a museum, the first open door is the entrance and, with the milk carton, the screw cap shouldn't be opened downwards. Just as we have learned these behaviors and viewing habits, most Internet users have also saved certain structures and forms. With page elements that are familiar to you, you can often find your way around an application much better than if all of the colors and shapes were suddenly swapped.
The logic of color
It is already "learned behavior " that a red answer field in a data entry process indicates an error and a green one indicates a success. Turning this around would be thinking about innovation in the wrong place. In order to avoid misleading of this kind and to understand what hinders the user and what encourages him, user experience designers use various tools and aids.
Don't forget: "User Testing"
In addition to reusing structures that I have learned, I can also ask users to test pages and drafts impartially, I can draw their attention to certain topics in advance, and I can track their behavior and get feedback. This prevents critical information from being overlooked or operations on the page not being carried out correctly. Without such information, users can jump too early from processes that are essential for the website provider.
“Design is not just what it looks like and feels like. Design is how it works.” -Steve Jobs
Imagine here, for example, that the registration or payment process is so awkward and lengthy that the customer loses interest or patience after 2/3 of the input fields. This leads to a direct (monetary) loss for the site operator, which can be prevented by taking into account a meaningful and pleasant user experience.
User interface design
Let's talk about the Design System first.
What is a design system?
A Design System is a collection of standards, patterns, and tools that are used to create a consistent and cohesive look and feel across a range of products and digital experiences. It provides a common visual language, style guide, and set of components for designers and developers to use when creating user interfaces.
A design system can include:
Brand Guidelines: The company's brand identity and messaging, including typography, color palettes, and imagery.
UI Components: A library of reusable UI elements, such as buttons, forms, and icons, that can be easily integrated into different products and experiences.
Style Guides: Detailed documentation of the visual design elements and how they should be used in different contexts.
Interaction Guidelines: The rules and guidelines for how UI elements should behave and respond to user interactions.
Accessibility Guidelines: Standards and best practices for making products accessible to users with disabilities.
The main goal of a design system is to create a consistent and recognizable look and feel across a company's products, while also making it easier and faster for designers and developers to create new experiences. By establishing a set of shared design principles and guidelines, a design system can help to ensure that a company's products are visually cohesive and user-friendly.
Why Design System important in User Interface Design (UI)?
Design systems are important in UI design for several reasons:
Consistency: Design systems ensure consistency in the look and feel of a company's products, creating a recognizable brand identity and making it easier for users to navigate and use the products.
Efficiency: Design systems provide pre-designed UI components and guidelines, reducing the time it takes for designers and developers to create new interfaces and speeding up the design and development process.
Scalability: A well-designed design system can be easily scaled and adapted as a company's product portfolio grows, making it easier to maintain a consistent look and feel across multiple products.
Collaboration: A design system can act as a shared language and set of tools for designers and developers, facilitating collaboration and reducing the risk of design inconsistencies.
Accessibility: Design systems often include accessibility guidelines, helping to ensure that products are usable for people with disabilities and meeting accessibility standards.
Improved User Experience: By providing a consistent and cohesive look and feel, a design system can enhance the overall user experience and increase user satisfaction.
In conclusion, design systems are critical in UI design because they help to create a consistent, efficient, and accessible user experience across multiple products and platforms.
How to design creative User Interfaces?
Designing a creative and effective user interface (UI) requires a combination of design skills, user research, and attention to detail. Here are some steps you can follow to design a creative UI:
Understand Your Users: Conduct user research to understand your users' needs, goals, and pain points. This will help you to create a UI that is tailored to their needs and provides a positive user experience.
Define Your Design Objectives: Clearly define what you want to achieve with your UI design, such as improving usability or making the product more visually appealing.
Create a Style Guide: Develop a style guide that defines the visual elements, such as color, typography, and imagery, that will be used in your UI design.
Choose the Right Layout: Choose an appropriate layout for your UI, such as a grid system or a flexible layout, and make sure it works well on different screen sizes and devices.
Use Appropriate Interaction Design: Use appropriate interaction design techniques, such as animations, microinteractions, and gestural navigation, to make your UI more engaging and interactive.
Pay Attention to Details: Pay close attention to the details, such as padding, margins, and typography, to ensure a consistent and cohesive look and feel throughout your UI.
Test and Iterate: Test your UI design with real users and gather feedback to iterate and improve your design.
In conclusion, designing a creative and effective UI requires a deep understanding of your users, a clear design objective, and a willingness to iterate and improve your design based on user feedback.
How to design a mobile User Interface (UI)?
Mobile User Interface (Mobile UI) refers to the graphical user interface (GUI) of mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets, that allow users to interact with the device's operating system and applications. The mobile UI design is an important aspect of the mobile user experience as it determines how users interact with the device and access its features and functionality.
Mobile UI design must be optimized for small screens and limited physical space, with considerations given to touch-based interactions, gestures, and the need for simplicity and ease of use. Mobile UIs typically use a combination of graphics, text, and icons to convey information and provide a clear and concise user experience.
Some common elements of mobile UI design include:
Touchscreen Navigation: Navigation through the mobile UI is typically performed through touch-based gestures, such as swiping, tapping, and pinching.
Icons and Graphics: Mobile UIs often use simple and easily recognizable graphics and icons to represent functions and features.
Minimalism: Mobile UIs often prioritize simplicity and minimalism to ensure ease of use on small screens and with limited physical space.
Contextual Awareness: Mobile UIs often use contextual awareness, such as location and device orientation, to provide a more personalized and relevant user experience.
Overall, mobile UI design must balance creativity, functionality, and simplicity to provide a user-friendly and accessible experience for mobile device users.
Note
If you are planning to have your own mobile application, website, or custom web app or have any type of query or concern regarding its concept, technical know-how, the best way to get it done then don’t hesitate to contact us at princepal@think360studio.com and we will provide you a free of consultation.
Skype: princepal-designer
Google Hangout: palprince@gmail.com
WhatsApp: +91 9915 106 790




